
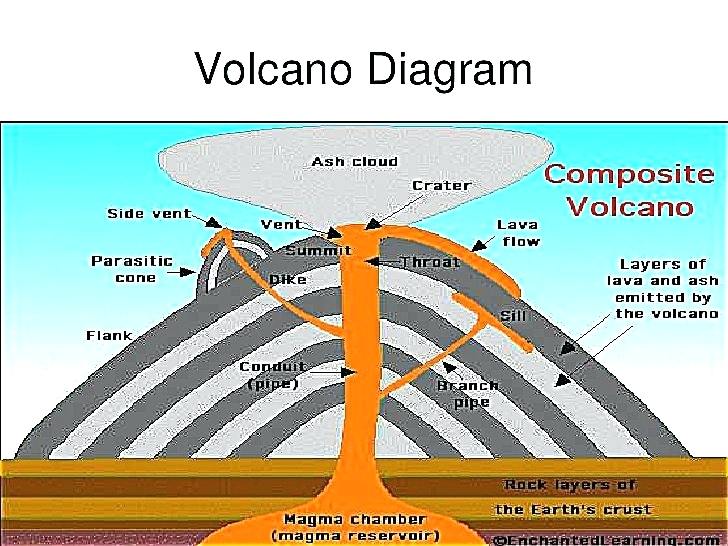
If you want to read more in depth information about active and new volcanoes, here is a link from Amazon to Volcanoes of the World. They can flood surrounding areas with successive flows, eventually forming plateaus.Ī well-known example of Shield Volcano is Maunaa Loa on the "Big" island in Hawaii. Some of these eruptions will pour basaltic lava from long fissures instead of central vents. Shield volcanoes have slopes from 10 degrees to 5 degrees at the top. These volcanoes tend to have large calderas at their summits.īecause they build up slowly through accretion, this type of volcano can be hundreds of miles across and can be on average 2,000 feet high. Therefore, Shield volcanoes form from nonexplosive eruptions of low viscosity magma.Īfter lava pours out in all directions from the central vent, or group of vents, it builds a broad, gentle sloping flat cone. These volcanoes have very little pyroclastic material. Shield volcanoes are mainly made of thin lava built in the central vent. To learn more, click here! Shield Volcanoes

Packed with information about eruptions, magma, source rocks, geothermal energy, and eruption effects on ecology.Ĭoral Reefs are likely to grow over the remains of underwater volcanoes. Paricutin Volcano in Mexico is another well studied example of a Cinder Cone Volcano.įor a comprehensive guide on volcanoes and detailed information on what is known about them, I suggest you get from Amazon The Encyclopedia of Volcanoes. Mount Etna in Sicily is covered with Cinder Cones. They are usually formed later in an eruption when activity has localized to one or more discrete vents. It is not uncommon to find Cinder cones as part, next, or at the flanks of other volcanoes. They are usually small volcanoes of about one mile in diameter and 1,000 feet high.Ĭinder Cones have steep sides and a small crater on top. Most cinder cones have a bowl shaped crater.Ĭinder cones are mainly made of accumulated, loose grainy cinders and almost no lava. These pieces dry and fall as pieces of cinder that accumulate near the vent forming a circular cone. When cinder volcanoes erupt, powerful blasts throw molten rocks, ash, and gas into the air. They are extrusive igneous rocks, that come from fragments of solidified lava. Hot Springs Cinder ConesĪ cinder (also called scoria) is pyroclastic material. If you are interested in experiencing geology in a more relaxed way, visit this map of U.S.
#Shield volcanoes diagrams full#
The book is full of illustrations and photos, explaining the origin of different geologic features around the world. If you would like to read a bit more about tectonic plates and about the geology of Earth, I suggest you get this book from Amazon called Origins: The Evolution of Continents, Oceans and Life. These areas also have volcanic activity due to the movement of magma. You can see them clearly in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean. This are usually divergent margins or where the tectonic plates are separating. In the map above the lighter shade of blue on the ocean floor represents lower depth. The same situation occurs on the other side of the Pacific, where Asia meets the Ocean Open Geology. The Plate under the Pacific Ocean is going underneath the South American Continent, creating the Andes mountains and a chain of volcanoes with it.
You can see in the map above, this margin is covered with volcanoes. This buoyant magma eventually migrates to the surface in the form of volcanoes.Ī clear example of this collision of plates is the Western Coast of South America. This molten magma is more bouyant than the material above. This material mixes and melts turning into liquid magma. The plate that sinks goes into great heat and pressure. This will result in a trench, and a lifting of a continental plate. In this collision one plate can go underneath the other. Like the East Coast of the United States.Īctive margins are sites where plates meet and collide. There are margins where the tectonic plates meet and there is no friction. This motion means that plates come together and spread apart. Convection currents under the plates move the plates in different directions. These plates move over the molten upper portion of the Earth's mantle. Plate Tectonics is a theory that explains how the Earth's outer most layer is divided into plates. These edges can be under land or under oceans. Most volcanoes are found at the edges of Tectonic Plates. If you like US geography, you might like this map of US Topography.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
